4.2 Carbon Lattice Force Fields
Currently there are 3 carbon force fields implemented in NanoCap. These are selected in the Calculations–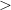 Carbon Lattice options as shown in Fig. 7.
Carbon Lattice options as shown in Fig. 7.
![\includegraphics[scale= 0.6]{../../screens/nanocap_carbon_lattice_options_win.png}](images/img-0037.png)
Each carbon force field is described below:
Unit Radius Topology
By default, when a carbon lattice is constructed a carbon force field is not used and the structure is simply a result of the triangulated dual lattice. This generates a topology of unit radius (cylindrical if a capped nanotube).
Scaled Topology
The simplest force field that produces a carbon structure of physical dimensions is the scaled topology force field. This forcefield uses the ideal C-C bond length of 1.421 to optimise the carbon lattice. The fictitious energy is given by the sum of squares deviation from this ideal bond length. This force field only does return derivatives and as such can only be used with the MC or SIMPLEX optimisers (see Section 5).
EDIP
The most sophistic force field implemented in NanoCap is the Environmental Dependence Interatomic Potential (EDIP). Using EDIP produces the most physically sound structures and its use is recommended. For a theoretical description of EDIP please refer to the following paper:
Generalizing the environment-dependent interaction potential for carbon
N. A. Marks Phys. Rev. B 63, 035401 2000
url: http://journals.aps.org/prb/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevB.63.035401